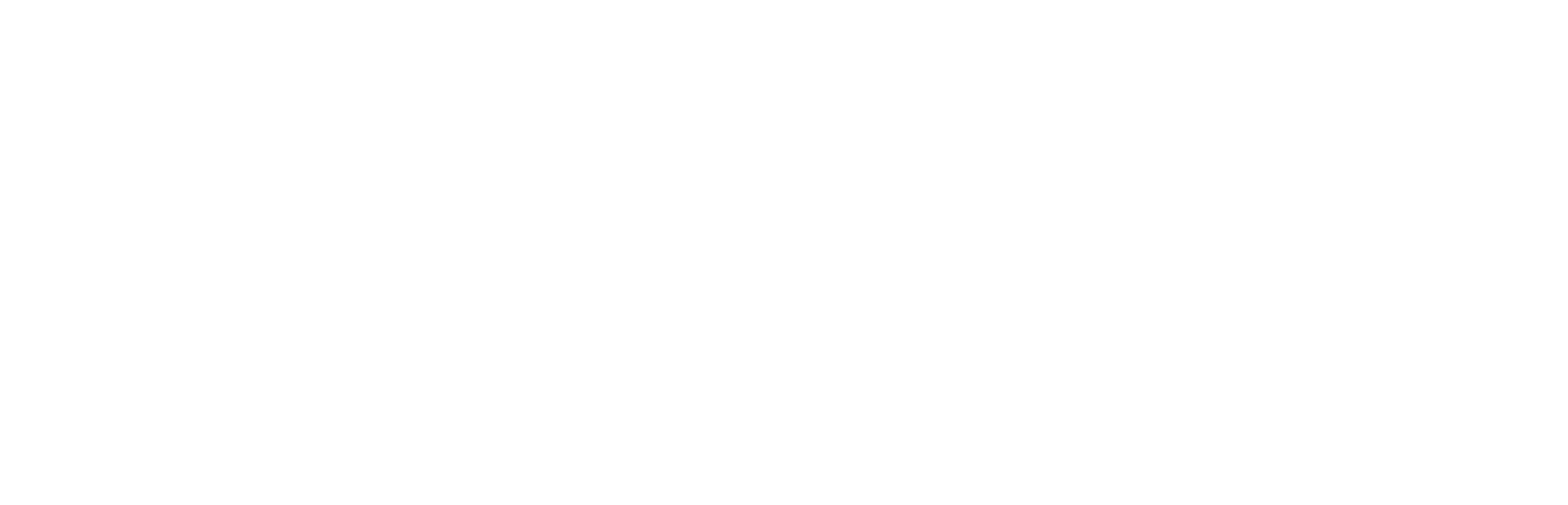
Antibiotic use can have knock-on results on the immune system
UrbanImages/Alamy
Kids uncovered to antibiotics within the womb or early in life don’t usually have an elevated threat of creating autoimmune circumstances in adolescence, in accordance with a research of greater than 6 million youngsters. However the relationship is sophisticated.
The concept that antibiotics may contribute to autoimmunity could be traced again to the Eighties, when David Strachan, then on the London Faculty of Hygiene and Tropical Drugs, recommended that fewer infections and cleaner environments might clarify rising charges of childhood allergy symptoms.
This led to the event of the hygiene speculation. This proposes that early publicity to sure microbes trains the immune system, stopping it from overreacting to innocent substances and inflicting allergic reactions or autoimmune circumstances. These circumstances, resembling sort 1 diabetes, inflammatory bowel illness and lupus, happen when immune cells inadvertently assault the physique’s personal tissues.
Since then, quite a few research have proven that many microbes – particularly these in our guts – form our immune system. As an illustration, some produce compounds which can be important for the event of specialized immune cells, known as regulatory T cells, which assist forestall autoimmunity. This has led to questions on whether or not antibiotics, which considerably alter the intestine microbiome, might contribute to the event of autoimmune circumstances.
“Over time, there was numerous pre-clinical work performed, principally in animal fashions, that strongly helps this notion that antibiotics, or modulation of the intestine microbiome, have a serious influence on our immunity,” says Martin Kriegel on the College of Münster in Germany.
For instance, a 2016 research in mice confirmed that repeated use of antibiotics early in life raises the chance of sort 1 diabetes. Mice genetically prone to the situation have been uncovered to an antibiotic 3 times – as soon as by means of their mom’s breastmilk and once more at 4 and 5 weeks previous. Round 50 per cent of male mice and 80 per cent of feminine mice on this group developed sort 1 diabetes by 30 weeks of age. By comparability, solely about 25 per cent of male mice and 50 per cent of feminine mice that weren’t uncovered to antibiotics developed the situation.
Human research have additionally hinted at a hyperlink. An evaluation of greater than 10 million individuals revealed earlier this yr discovered that these prescribed an antibiotic had a 40 per cent better threat, on common, of later being recognized with inflammatory bowel illness. In the meantime, a 2019 research of greater than 110,000 individuals discovered that antibiotic prescriptions have been related to a 60 per cent larger probability of creating rheumatoid arthritis.
However different analysis has proven the other. As an illustration, a 2017 research of greater than 15,000 youngsters examined for sort 1 diabetes or coeliac illness discovered no affiliation between the event of those circumstances and using antibiotics earlier than 4 years of age.
Most lately, Eun-young Choi at Sungkyunkwan College in South Korea and her colleagues tracked incidences of six autoimmune circumstances – sort 1 diabetes, continual childhood arthritis, ulcerative colitis, Crohn’s illness, lupus and Hashimoto’s illness – in additional than 2.6 million youngsters whose moms had an an infection throughout being pregnant. About 1.5 million of their moms have been prescribed antibiotics whereas pregnant. The researchers then did the identical in a separate group of three.4 million youngsters who had an an infection inside six months of being born, 1.9 million of whom have been handled with an antibiotic.
After accounting for elements resembling an infection sort, socioeconomic standing and intercourse, the researchers discovered no total affiliation between youngsters’s publicity to antibiotics in utero or early childhood and later threat of creating an autoimmune situation in adolescence.
So why is there a lot discrepancy between research? The issue is, the intestine microbiome is extraordinarily advanced. All kinds of things affect it, making it practically unattainable for researchers to account for all of them. As an illustration, not one of the research talked about above adjusted for weight-reduction plan, which can considerably alter intestine microbiota.
Completely different antibiotics might also have totally different results. As an illustration, Choi and her staff did discover an affiliation between using broad-spectrum antibiotics throughout being pregnant and youngsters later creating Crohn’s illness. Members’ age at publicity additionally appeared to matter. These prescribed antibiotics inside two months of delivery had a 30 per cent better threat of Hashimoto’s illness.
This doesn’t imply we must always forgo antibiotics. “When antibiotic use in being pregnant is really useful, it’s as a result of proof means that the advantages outweigh the doable dangers,” Christopher Zahn on the American School of Obstetricians and Gynecologists in Washington DC. For instance, urinary tract infections elevate the chance of untimely delivery, low delivery weight and critical problems, resembling sepsis, he says.
Some antibiotics might even shield in opposition to autoimmunity. A 2018 research discovered that an infection with the pathogenic micro organism Enterococcus gallinarum triggered autoimmunity in mice predisposed to such circumstances. Treating them with antibiotics not solely prevented them from dying but in addition stopped their immune cells from attacking their physique.
“So it’s all simply terribly advanced,” says Kriegel.
Nonetheless, the latest findings ought to present reassurance about antibiotics for individuals who are pregnant or have younger youngsters, says Zahn.
Matters: