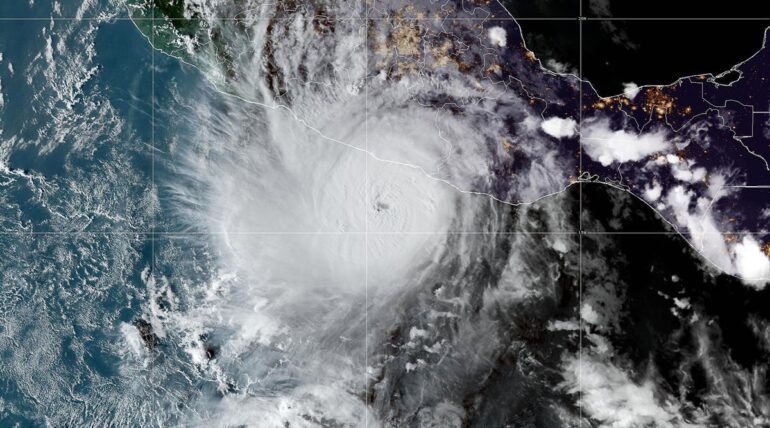
On tv broadcasts and forecast maps, hurricanes seem as two-dimensional swirling vortices, belying their extraordinarily complicated three-dimensional construction. Having the ability to peer previous the tops of clouds to see what’s taking place inside a storm is crucial for forecasting—significantly for catching one that’s about to quickly intensify into one thing extra harmful. However a key supply of information that present an x-ray-like view of that construction will shut down by June 30, simply earlier than hurricane season tends to kick into excessive gear.
“It’s definitely one of many extra essential knowledge sources that we now have as a result of it supplies a singular dataset,” says James Franklin, former chief of the Nationwide Hurricane Heart’s (NHC’s) Hurricane Specialist Unit. “It’s the one manner actually to see by clouds and get a way of the organizational construction of the core of a growing cyclone.” Having that info can alert forecasters to speedy intensification or different main adjustments hours earlier than they turn out to be obvious in different knowledge—offering essential time to warn folks in hurt’s manner.
This view into storm construction comes from sensors onboard Protection Meteorological Satellite tv for pc Program (DMSP) satellites. These knowledge will not be taken up, processed and despatched out to the Nationwide Hurricane Heart or different non-Division of Protection customers. The precise causes for the shutoff are unclear however seem like associated to safety issues.
On supporting science journalism
Should you’re having fun with this text, contemplate supporting our award-winning journalism by subscribing. By buying a subscription you might be serving to to make sure the way forward for impactful tales concerning the discoveries and concepts shaping our world as we speak.
“The timing [of the shutdown] couldn’t be worse so far as hurricane season is worried,” and it comes together with different current cuts and limitations to the Nationwide Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration, says Kim Wooden, an atmospheric scientist on the College of Arizona.
What do microwave knowledge inform us about hurricanes?
Satellites orbiting the Earth collect knowledge in a number of wavelengths of sunshine: seen, infrared, microwave, and so forth. Every supplies totally different sorts of data. Most individuals usually see pictures of hurricanes within the seen a part of the electromagnetic spectrum, however the storms additionally emit microwaves. “The whole lot is emitting microwaves,” Wooden says. “We’re at present emitting microwaves sitting right here. And it’s as a result of our temperatures are above absolute zero.”
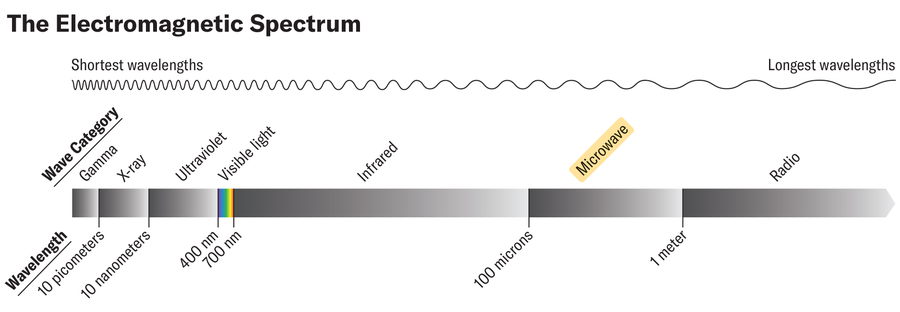
Microwaves are helpful in monitoring hurricanes, Wooden says, “as a result of the waves are so lengthy they get by the tops of the clouds.” This lets forecasters see a storm’s internal workings—significantly adjustments to its eye and eye wall (the circle of clouds that encompass the attention and make up the strongest a part of the storm). Such adjustments can point out if a hurricane is strengthening or weakening.
It is a significantly great tool for monitoring storms at evening, when seen satellite tv for pc imagery is unavailable. Although infrared knowledge can be found at evening, microwave knowledge have 16 occasions their decision, Wooden says. Having the ability to watch a storm in a single day may also help keep away from what Franklin calls a “dawn shock”—when forecasters get the primary seen imagery at daylight and discover that the storm has turn out to be a lot stronger or higher organized than that they had anticipated.
Microwave imagery is especially helpful for catching speedy intensification—outlined as when a storm’s winds soar by not less than 35 miles per hour in 24 hours. Forecasters utilizing microwave knowledge can catch the method and warn folks sooner than they may in any other case. This was the case with Hurricane Otis in 2023, which was the primary recognized Class 5 Pacific hurricane ever to make landfall and precipitated vital devastation. Microwave “satellite tv for pc imagery clued us in to the potential for this method to be actually sturdy,” Wooden says.
Microwave knowledge are additionally extraordinarily helpful in finding the middle of weaker storms. These storms are likely to lack a central eye and eye wall, and clouds increased within the ambiance can obscure the place these situated decrease down are circulating in seen imagery. Understanding the place the middle of the storm lies is essential info to feed into hurricane fashions that forecast the place the storm will go. Feeding microwave knowledge into fashions can enhance the accuracy with which they decide the place of the middle of a storm by about 60 miles, Franklin says—noting that an incorrect place is “going to cascade or leak into your observe forecast.” Which means that meteorologists who lack microwave imagery could not be capable of forecast the place a storm will make landfall as precisely as those that have it.
The place do microwave knowledge come from, and why had been they minimize?
As a result of the microwaves emitted from Earth’s floor and ambiance are very weak, they’ll solely be detected by satellites in very low-Earth orbit, Wooden says. (The geostationary satellites that present seen imagery orbit farther out. To have a sensor large enough to detect microwaves from their place, they might have to be the scale of the Loss of life Star, Wooden says.) However as a result of these microwave-detecting satellites orbit so near Earth, they see much less of it at any given time than geostationary satellites do—so extra of them are wanted to adequately monitor the planet. And there are longer time gaps between when a microwave-detecting satellite tv for pc “revisits” the identical spot.
Which means microwave knowledge are already restricted. There are at present six satellites offering that info for U.S. climate forecasting functions, and they’re solely helpful for hurricanes in the event that they serendipitously move overhead on the proper time. However now three of them are about to be turned off. “That’s an enormous drop within the availability of this software,” Franklin says.
The information which can be about to be misplaced come from what are known as Particular Sensor Microwave Imager Sounder (SSMIS) sensors onboard three DMSP satellites. The precise motive for the shutoff is unclear, although some experiences have cited safety issues. It doesn’t seem that the issues are with sharing the information themselves or with funding the gathering and dissemination of that info.
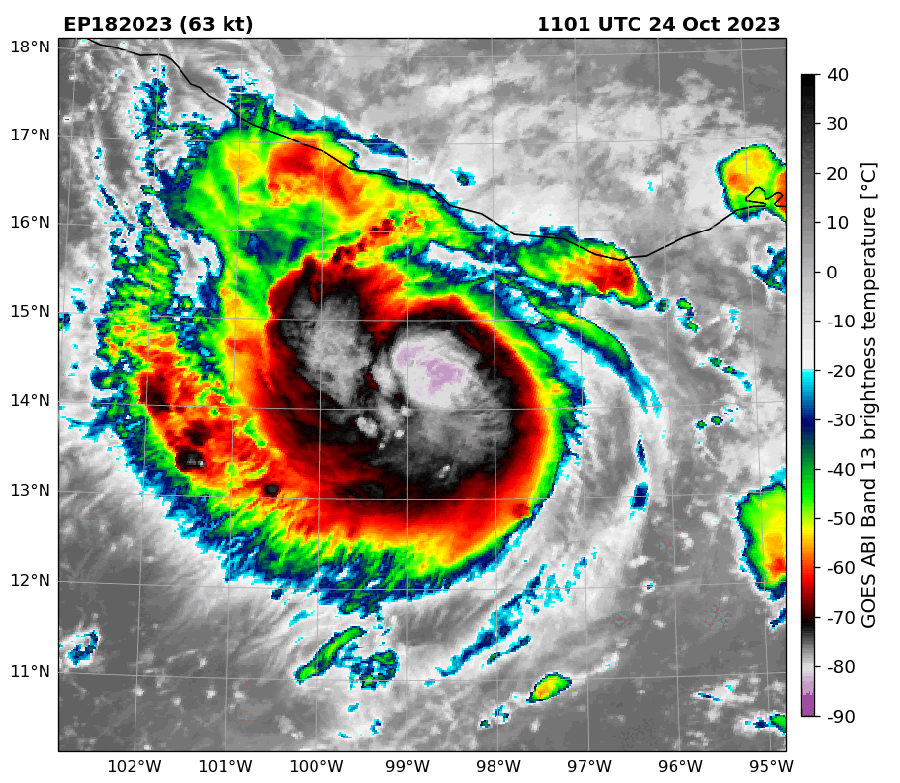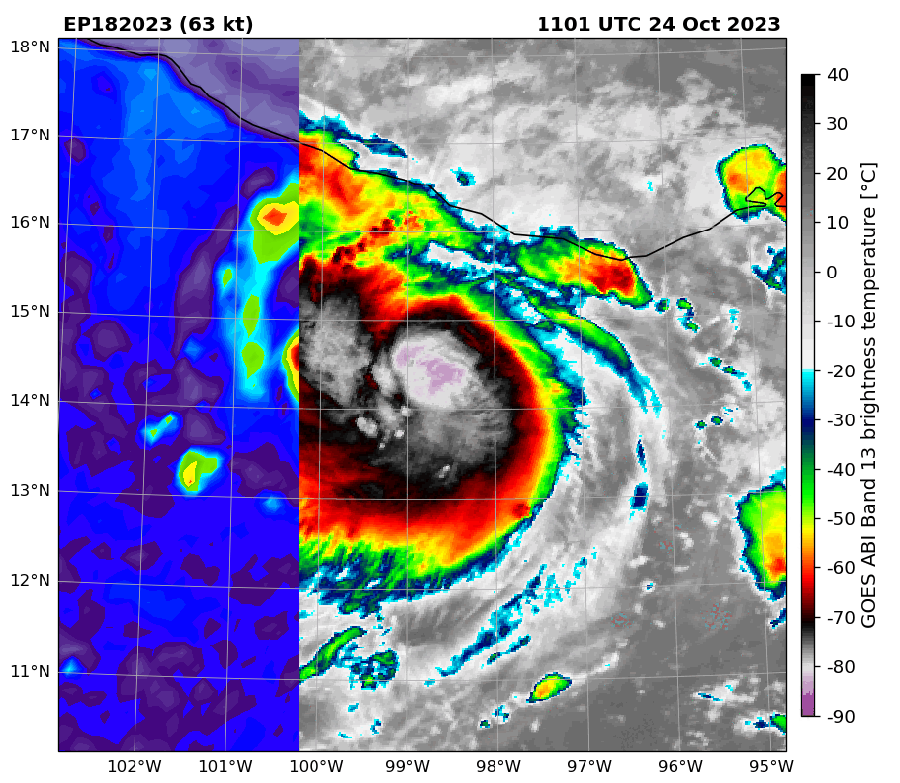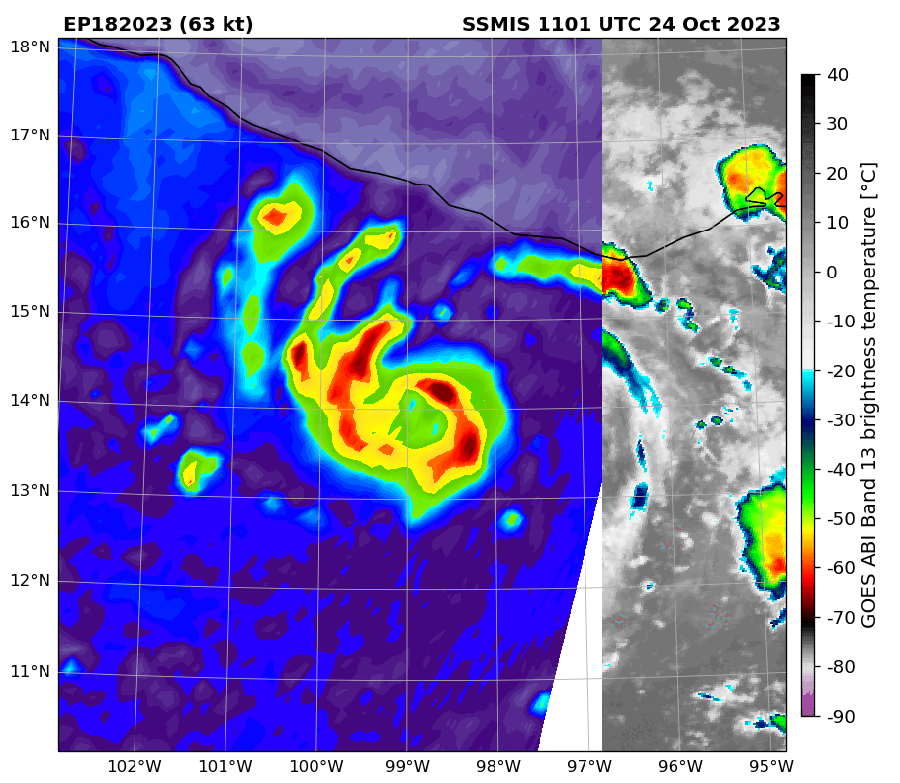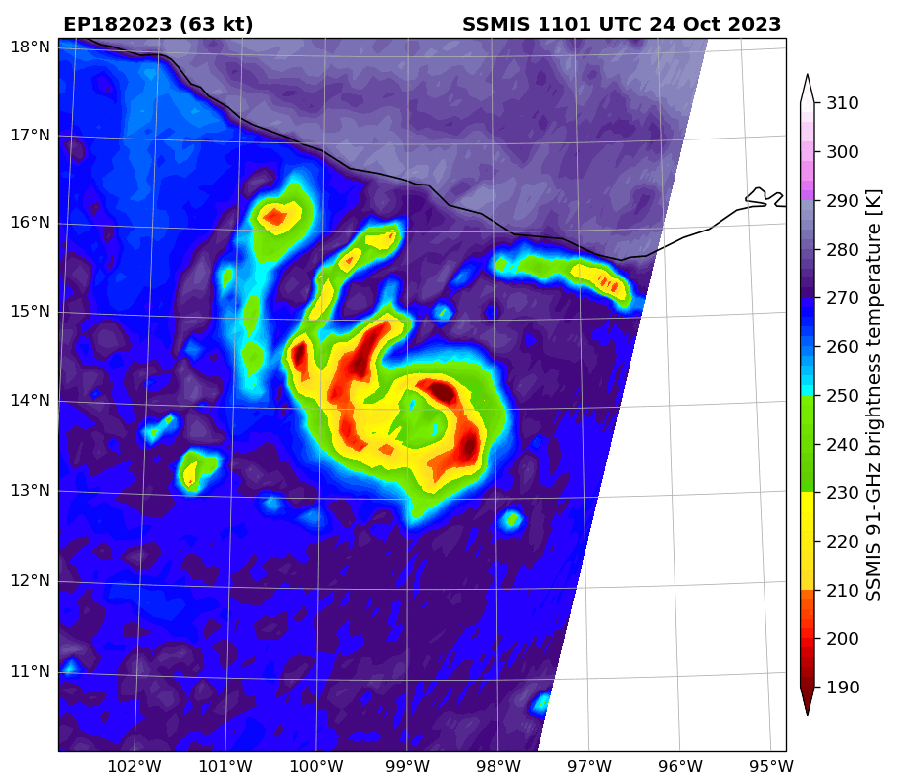
Infrared satellite tv for pc imagery of Hurricane Otis in comparison with microwave imagery. Within the later, the middle of the storm is extra seen and signifies the hurricane was strengthening.
In an e-mail to Scientific American, a spokesperson for the U.S. Area Drive wrote that “DMSP satellites and devices are nonetheless practical” and that DOD customers will proceed to obtain the information. They referred additional questions concerning the resolution to the U.S. Navy, which had not replied to requests for remark by press time.
In an e-mail to Scientific American, Maria Torres, a spokesperson for the NHC, wrote that “the DMSP is a single dataset in a strong suite of hurricane forecasting and modeling instruments within the NWS portfolio.” She cited different satellites, ocean buoys and the Hurricane Hunter flights, amongst different instruments. “NOAA’s knowledge sources are absolutely able to offering an entire suite of cutting-edge knowledge and fashions that make sure the gold-standard climate forecasting the American folks deserve,” Torres wrote.
There are different satellites that might theoretically present microwave knowledge—together with a just lately launched DOD satellite tv for pc—however there was no dialogue of constructing these knowledge broadly accessible, Wooden says. And since forecasting fashions and different programs are geared towards the present knowledge, it isn’t easy to make use of a brand new knowledge supply instead. “It’s one factor for a satellite tv for pc to exist,” Woods say. “It’s one other factor for us to have the ability to entry it.”
What we are able to anticipate this hurricane season
The lack of these knowledge is most regarding in relation to storms which can be comparatively far out within the ocean (past the vary of Hurricane Hunter plane) and to storms within the Pacific Ocean, the place fewer such missions are flown. There are usually extra monitoring flights for storms which can be a menace to the U.S., significantly as they get near land. However two thirds of all hurricane advisories are issued primarily based solely on satellite tv for pc knowledge, Franklin says.
The lack of these knowledge alone could be extraordinarily regarding for forecast accuracy this hurricane season—but it surely comes on prime of the broader cuts which have already been made to the Nationwide Climate Service and NOAA. For instance, there could also be fewer launches of the climate balloons that assist illuminate how the bigger atmospheric setting will steer a storm. And it’s unclear if Hurricane Hunter flights may be affected. “Dropping this knowledge is worse than it may need been a 12 months in the past,” Wooden says.
“It’s just about assured that there can be some forecast this 12 months the place vital intensification, almost certainly of a tropical storm [to a hurricane], is missed by six to 12 hours as a result of these knowledge weren’t out there,” Franklin says. If it’s a Pacific Coast storm, this may very well be devastating for communities in the best way. And even whether it is out at sea, it’s a large concern for mariners. “Ships go down in hurricanes,” Franklin says.
All in all, “there are a number of issues which can be working in opposition to forecasting” this 12 months, he says.