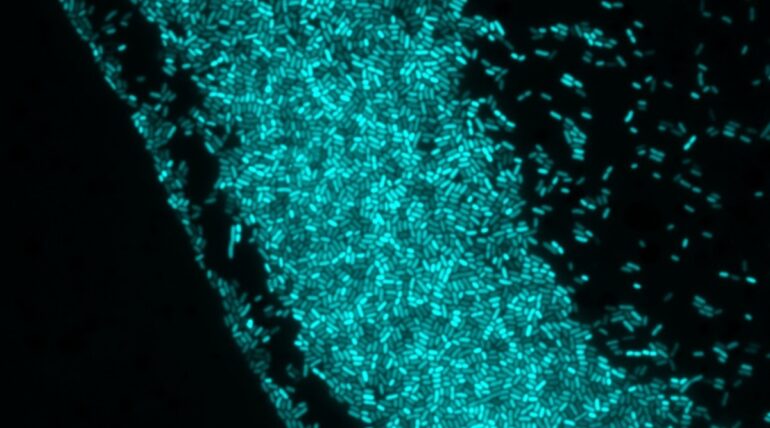
Micro organism wouldn’t be so dangerous if we might inform them what to do. “Cease spreading! Cease sticking collectively! Cease warding off our antibiotics!” A brand new technique is beginning to enable scientists to just do that, letting them use mild to regulate sure capabilities of micro organism.
Launched in a paper revealed in The European Bodily Journal Plus, the preliminary strategy might have a number of potential functions, together with a doable avenue for combating antibiotic resistance.
The Drawback of Antibacterial Resistance
Micro organism are behind a wide range of ailments, from strep to staph to pneumonia and meningitis, they usually assault our our bodies in a wide range of methods, as effectively, together with by way of the manufacturing of poisons that injury and disrupt our cells. A few of these infections cease on their very own, however others are too cussed, or too severe, to depart untreated. These are the infections that we goal with antibiotics — that’s, so long as our antibiotics are working.
However, as a result of micro organism are consistently altering, they’ll develop defenses towards the antibiotics that we use to stave them off, making these therapies a lot much less efficient. That’s the gist of the rising risk posed by antibiotic resistance, which has contributed to tens of millions of deaths since 1990 and is anticipated to contribute to tens of millions extra by 2050.
Getting down to discover a new resolution to this rising drawback, scientists from the Italian Institute of Expertise and the Polytechnic College of Milan launched into the Engineering of Micro organism to See Mild (EOS) venture. The venture goals to make use of mild to regulate micro organism, primarily for the battle towards antibiotic resistance. And the brand new technique pushes the venture nearer to attaining that goal.
Utilizing mild and light-sensitive molecules to regulate {the electrical} alerts which might be transmitted throughout the bacterial membrane, the strategy impacts the organic exercise of micro organism with none alterations to their genetic make-up.
“This interaction between mild and electrical [signaling] permits us to regulate key organic processes corresponding to motion, biofilm formation, and antibiotic sensitivity,” stated Giuseppe Maria Paternò, a research writer and a professor on the Polytechnic College of Milan, in keeping with a press launch. “We are able to affect antibiotic uptake and restore and even improve the effectiveness of therapies towards resistant strains.”
Learn Extra: Antibiotic-Resistant Micro organism: What They Are and How Scientists Are Combating Them
Coating Micro organism to Curb Antibiotic Resistance
To manage micro organism, the strategy takes benefit of a light-sensitive molecule referred to as Ziapin2, which sticks to the bacterial floor. By overlaying micro organism with this light-sensitive molecule and by subjecting the lined micro organism to mild, the scientists have been in a position to modify {the electrical} alerts that have been transmitted throughout their bacterial membranes, remodeling the micro organism’s primary functioning.
Testing their technique on one of the vital studied bacterial species, the scientists modified {the electrical} signaling throughout the membranes of Bacillus subtilis, a well-liked mannequin organism that’s usually used as a stand-in for Staphylococcus aureus, the bacterium that causes staphylococcus, or staph, infections.
When examined, the strategy modulated the micro organism’s susceptibility to Kanamycin, an intracellular antibiotic that’s incessantly used as a therapy for extreme bacterial infections after different therapies fail.
“Underneath blue mild,” Paternò stated within the launch, “the effectiveness of Kanamycin was considerably diminished,” indicating that {the electrical} signaling on the bacterial membrane “performs an important function within the drug’s uptake.”
Further analysis is required to tailor the strategy to extend the effectiveness of Kanamycin and different antibiotics towards micro organism. However for now, evidently such an final result could possibly be doable.
“This preliminary evaluation […] represents a primary step in a very new discipline of research,” the scientists state of their paper. “This proof-of-concept research underscores the potential of non-genetic, light-based interventions to modulate bacterial susceptibility in actual time. Future work will broaden this strategy […] in the end advancing our understanding of bacterial bioelectric regulation and its functions in antimicrobial therapies.”
This text shouldn’t be providing medical recommendation and ought to be used for informational functions solely.
Learn Extra: Researchers Make Pc Fashions To Sort out Antibiotic Resistance
Article Sources
Our writers at Discovermagazine.com use peer-reviewed research and high-quality sources for our articles, and our editors evaluate for scientific accuracy and editorial requirements. Evaluation the sources used under for this text:
Sam Walters is a journalist overlaying archaeology, paleontology, ecology, and evolution for Uncover, together with an assortment of different subjects. Earlier than becoming a member of the Uncover workforce as an assistant editor in 2022, Sam studied journalism at Northwestern College in Evanston, Illinois.