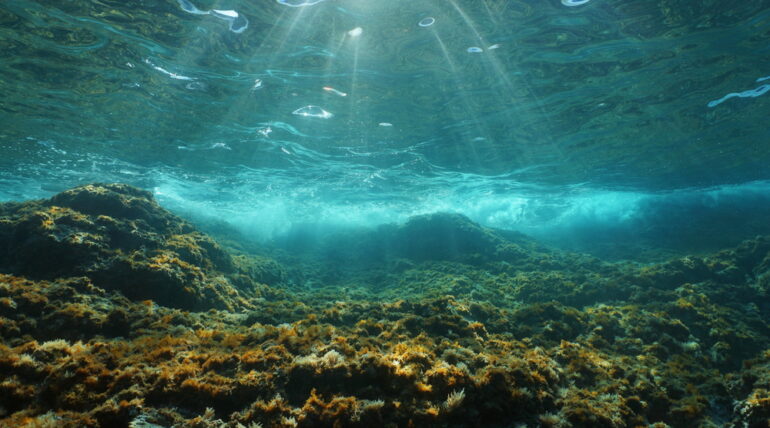
The biggest identified flood in geological time took wherever from 2 years to 16 years to refill the Mediterranean Sea. Whereas it didn’t refill the realm quick, the water was highly effective and hit some areas at speeds of 67 miles per hour — unleashing a wall of destruction that dug out canyons, formed future islands and worn out greater than 95 % of identified marine species on the time.
“What makes this occasion extraordinary is it’s the largest flood that we all know that ever occurred in Earth’s historical past,” says Aaron Micallef, a marine geoscientist at Monterey Bay Aquarium Analysis Institute, a nonprofit oceanography heart. “It was maybe essentially the most dramatic even that our planet witnessed since 65 million years in the past when the meteor hit Mexico’s Yucatan and led, amongst different issues, to the demise of the dinosaurs.”
The Zanclean Megaflood
Scientists have argued a while over that the Mediterranean skilled an enormous flood brought on by an inflow of water coming by means of the slender Strait of Gibraltar. The strait, the place Spain is just a few miles away from the coast of Morocco, was blocked up round 6 million years in the past, isolating the Mediterranean from the remainder of the Atlantic Ocean. The Mediterranean started to dry up and empty out, leaving two smaller basins within the east and west, sitting roughly on both aspect of Sicily and Malta.
“Mainly, you may stroll from Libya to Italy, or no matter was there on the time,” Micallef says.
However a lot of the Mediterranean remained beneath sea degree, creating the recipe for a disaster. This occurred round 5.3 million years in the past, when the Atlantic breached the Strait of Gibraltar as soon as once more, filling up the 2 basins to make what we all know at present because the Mediterranean Sea. The occasion is called the Zanclean megaflood.
The difficulty is, a lot of the earlier proof got here from salt deposits — some kilometers thick — on the Mediterranean seafloor — a sign of what scientists name the Messinian salinity disaster. These have been salt deposits that have been left on the bottom because the seawater dried up. However some questioned whether or not these salt traces may have been brought on by different sources.
Learn Extra: Unsung and Underwater: 5 Sunken Cities From European Seas
Proof of the Huge Flood
In 2018, Micallef and his colleagues printed a examine saying the invention of huge sediment deposits to the southeast of Sicily and east of Malta much like what was left by an enormous flood. In addition they found an underwater canyon — one of many largest of the world — that was doubtless carved out by the tsunami-like flood.
“This channel is one thing you wouldn’t anticipate in such a shallow space,” he says.
In a extra current examine printed just a few months in the past in Communications Earth and Atmosphere, Micallef and his colleagues went on land to seek out proof of the Zanclean flood. The workforce descried as much as 300 elongated ridges discovered throughout the complete area of southern Sicily.
“These ridges are largely oriented in the identical route as you’d anticipate the flood to be,” Micallef says.
Quite a lot of the outcrops had unusual options, and have been made up of gravel, pebbles, and even bigger stones that might have required a strong surge of water to move all of them to the realm.
Filling the Mediterranean Sea
The refilling of the ocean occurred in spurts. Water was doubtless leaking by means of the Strait of Gibraltar for a while earlier than it was totally breached, Micallef says. However when the flood got here, it got here quick — maybe as a lot as 50 meters per second (67 miles per hour) in some elements.
“That might be virtually like a tsunami,” Micallef says — it will have been bigger and extra damaging.
This water carried large ranges of deposit, the type Micallef and his colleagues found southeast of Sicily, and carved underwater canyons with a big underwater channel off the Mediterranean coast of Morocco, he says.
There would have been no escaping its path, for each marine or land creatures. In truth, one examine estimated that of two,006 marine species identified to have lived within the Mediterranean when it was remoted, solely 86 survived extirpation.
“Solely 4 % of marine species made it,” Micallef says.
However whereas among the flood occurred rapidly, the Mediterranean most likely didn’t stabilize and refill utterly for wherever from two to 16 years, Micallef mentioned. Some days the ocean degree might have risen 32 toes, he says.
Learn Extra: Early People Doubtless Used Dugout Canoes to Journey the Open Sea 8,500 Years In the past
Europe and North Africa Evolution
For Micallef, studying extra about this flood can train us how fashionable Europe and North Africa developed, biologically and geologically. The flood doubtless affected the entire world, inflicting large-scale modifications for the local weather as effectively.
But in addition, studying concerning the damaging forces unleashed by such a flood can train us extra about what may occur when giant glacial lakes burst on account of local weather change-driven ice melting.
Article Sources
Our writers at Discovermagazine.com use peer-reviewed research and high-quality sources for our articles, and our editors evaluation for scientific accuracy and editorial requirements. Assessment the sources used beneath for this text:
Joshua Rapp Be taught is an award-winning D.C.-based science author. An expat Albertan, he contributes to various science publications like Nationwide Geographic, The New York Occasions, The Guardian, New Scientist, Hakai, and others.