A brand new method to Alzheimer’s illness remedy may very well be on the horizon, impressed by a compound present in frequent herbs.
Carnosic acid is present in rosemary and sage and is thought for its antioxidant and anti inflammatory properties; nonetheless, it’s unstable in its pure kind.
Now researchers in California have synthesized a secure spinoff of the compound, which confirmed promising ends in mouse fashions of Alzheimer’s.
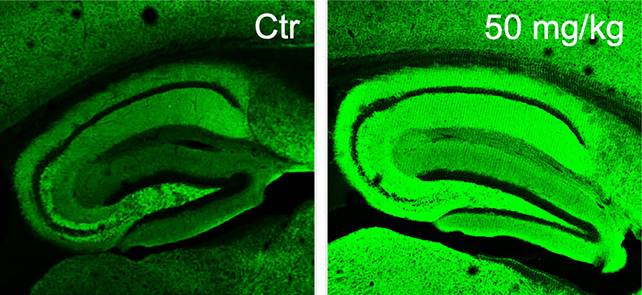
Mice that got the secure spinoff had boosts in reminiscence, extra neuron synapses, decreased irritation, and extra elimination of poisonous proteins which can be linked to Alzheimer’s.
That covers a number of indicators of Alzheimer’s illness, which might kill off a excessive proportion of synapses, breaking key neuron communication routes, whereas reminiscence loss is without doubt one of the most noticeable results.
“We did a number of completely different checks of reminiscence, they usually had been all improved with the drug,” says neuroscientist Stuart Lipton, from the Scripps Analysis Institute.
“It did not simply decelerate the decline, it improved just about again to regular.”
One of many most important challenges confronted by the researchers was getting carnosic acid right into a secure kind that will final lengthy sufficient within the mind to have an impact. After in depth checks, they discovered an appropriate di-acetylated kind (diAcCA).
The intestine converts diAcCA to carnosic acid earlier than it enters the bloodstream, the place they discovered it has about 20 p.c higher absorption than pure carnosic acid. As soon as transformed, the carnosic acid reached therapeutic ranges within the mind inside an hour.
Mice with a type of Alzheimer’s had been then given diAcCA or a placebo thrice per week for 3 months. The researchers appeared on the results on mind tissue and the way nicely the mice did on workouts designed to assess their reminiscence and talent to be taught.
The diAcCA compound did not seem to have any poisonous results on the mice handled with it, and extreme buildups of proteins identified to be indicators of Alzheimer’s injury had been decreased of their brains.
“By combating irritation and oxidative stress with this diAcCA compound, we truly elevated the variety of synapses within the mind,” says Lipton.
“We additionally took down different misfolded or aggregated proteins comparable to phosphorylated tau and amyloid beta, that are thought to set off Alzheimer’s illness and function biomarkers of the illness course of.”
It is all very promising, though we’re nonetheless on the early phases right here. Scientific trials can be wanted to verify that diAcCA has the identical results in human brains.
Given the anti-inflammatory properties of carnosic acid, which have additionally been recorded in earlier research, Lipton and his colleagues are hopeful that this identical remedy may very well be used for different situations linked to irritation – from sort 2 diabetes to Parkinson’s.
There’s additionally potential for diAcCA medication for use alongside different therapies for Alzheimer’s that are actually out there. As this compound is a modified type of carnosic acid – already identified to be protected for consumption – the researchers are hoping new medicines might be developed on an accelerated schedule.
“It may make current amyloid antibody therapies work higher by taking away or limiting their uncomfortable side effects,” says Lipton.
The analysis has been revealed in Antioxidants.