After a current fossil discovery, we now have new insights into the behaviors of a bunch of prehistoric people.
A staff of worldwide researchers working with the Evolutionary Research Institute on the College of Witwatersand have uncovered a serious discover about early human ancestors. In a research revealed in The Journal of Human Evolution, it’s revealed that Paranthropus robustus, a species of prehistoric human, have been bipedal and walked upright very like we do as we speak.
This discovering helps scientists be taught extra in regards to the each day lives and actions of Paranthropus robustus and provides extra complexity to the story of human evolution.
A New Prehistoric Ancestor
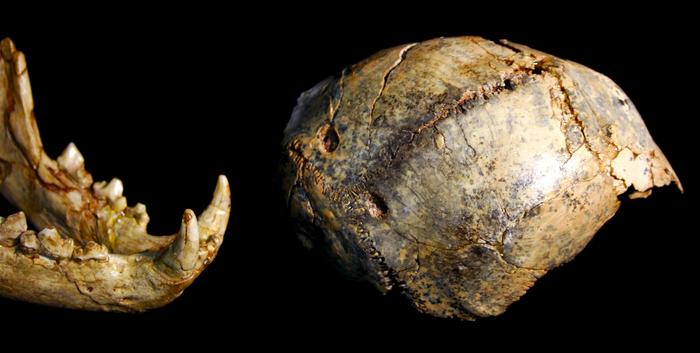
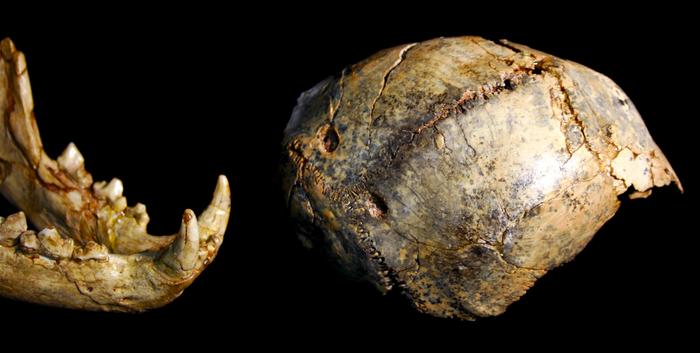
Though scientists have been researching the fossil stays of Paranthropus robustus for the reason that Nineteen Forties, they nonetheless had a slender understanding of the species’ stature, posture, and mobility. The brand new fossil findings, which embrace a hipbone, thigh bone, and shin bone, change that.
The group of fossils, belonging to a single, younger grownup, show that Paranthropus robustus have been recurring upright walkers, very like fashionable people and their Homo ergaster neighbors. The brand new discovery additionally confirms that this species of prehistoric human was extremely small.
In a press launch, Professor Pickering from the College of Wisconsin-Madison estimates that “this particular person, most likely a feminine, was solely a couple of meter tall and 27 kg (60 lbs) when it died, making it even smaller than adults from different diminutive early human species, together with these represented by the well-known ‘Lucy.’”
The brand new fossils have additionally confirmed one other suspicion about Paranthropus robustus. Scientists theorized that this species’ small stature seemingly made them at excessive danger for assaults from native predators, like sabertooth cats and big hyenas. Harm on the floor of the current fossil finds affirm this concept, as they present proof of tooth marks and chewing harm made by leopards.
Learn Extra: How Leopard Kills Rewrite Our Prehistory
Who Are Paranthropus robustus?
Paranthropus robustus are a prehistoric human group who lived in South Africa about two million years in the past. Additionally they lived alongside Homo ergaster, the direct ancestor of recent people.
Proof of their existence is commonly present in Swartkrans Cave, which is situated between Johannesburg and Pretoria, and there’s a lot of proof!
Up till now, many of the fossils discovered from this group are skulls and enamel. These fossils have been extremely insightful for scientists, who’ve been capable of piece collectively numerous details about Paranthropus robustus’ food plan and social group.
For instance, a number of the fossils have indicated that this prehistoric group was capable of survive in conditions the place meals high quality was low. Their heavy jaws and durable enamel would’ve allowed them to eat meals that was troublesome to chew in instances when extra digestible meals was in brief provide.
Moreover, lots of the skulls and enamel discovered are unusually massive. The fossil dimension reveals that this prehistoric society would’ve been made up of enormous males and small females. This organizational construction additionally means that they seemingly participated in polygyny, a mating system the place one dominant male would mate with a number of females.
Future Analysis
There’s nonetheless a lot for scientists to find out about this prehistoric inhabitants. Paranthropus robustus fossils are sometimes discovered inside shut proximity to bone and stone instruments. One huge query researchers have is whether or not or not these instruments have been made by this species, by neighboring species, like Homo ergaster, or by each.
The analysis staff behind this discovery additionally plans to proceed investigating the brand new fossils utilizing CT-scan analyses. They hope these analyses will present further perception into Paranthripus robustus’ patterns of progress and growth and can add extra particulars to the story of how they lived.
Learn Extra: Two-Million-12 months-Outdated Tooth Widens the Historical Human Household Tree
Article Sources
Our writers at Discovermagazine.com use peer-reviewed research and high-quality sources for our articles, and our editors overview for scientific accuracy and editorial requirements. Assessment the sources used beneath for this text:
Because the advertising coordinator at Uncover Journal, Stephanie Edwards interacts with readers throughout Uncover’s social media channels and writes digital content material. Offline, she is a contract lecturer in English & Cultural Research at Lakehead College, instructing programs on every little thing from skilled communication to Taylor Swift, and acquired her graduate levels in the identical division from McMaster College. Yow will discover extra of her science writing in Lab Supervisor and her brief fiction in anthologies and literary journal throughout the horror style.