Within the Milky Manner’s central bulge, about 24,000 light-years from Earth, a peculiar pair of objects seems to be hurtling by way of house at breakneck pace.
Proof suggests these objects are a high-velocity star and its accompanying exoplanet, a brand new examine stories. If that is confirmed, it will set a brand new document because the fastest-moving exoplanet system recognized to science.
Stars are on the transfer all through the Milky Manner, usually at a couple of hundred thousand miles per hour. Our Photo voltaic System’s common velocity by way of the galaxy’s Orion Arm is 450,000 miles per hour, or 200 kilometers per second.
These two objects are careening twice as quick, at a pace of no less than 1.2 million miles per hour (540 kilometers per second).
“We predict it is a so-called super-Neptune world orbiting a low-mass star at a distance that may lie between the orbits of Venus and Earth if it had been in our photo voltaic system,” says astronomer Sean Terry from the College of Maryland and NASA’s Goddard Area Flight Heart.
“In that case, will probably be the primary planet ever discovered orbiting a hypervelocity star.”
The 2 objects had been initially present in 2011, as researchers hunted exoplanets in knowledge from Microlensing Observations in Astrophysics (MOA), a undertaking primarily based on the College of Canterbury Mount John Observatory in New Zealand.
Gravitational microlensing is a phenomenon that happens when an enormous celestial object is close to the road of sight that runs between a distant observer on one facet and a distant star on the opposite.
Since mass warps spacetime, the star’s mild curves because it passes by way of the thing’s distorted spacetime on its method to the observer. If all three factors align carefully sufficient, the bent spacetime across the center object acts as a lens for the observer, amplifying starlight.
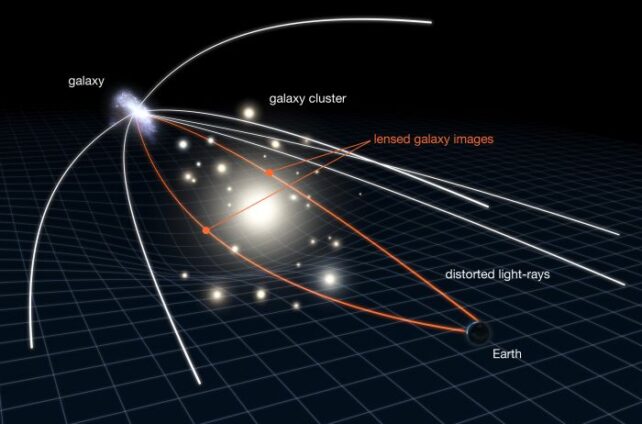
Researchers learning MOA knowledge in 2011 decided the objects’ relative mass – one is 2,300 instances extra huge than the opposite – however the precise mass of each remained unclear.
“Figuring out the mass ratio is straightforward,” says astronomer David Bennett from the College of Maryland and NASA Goddard, who labored on the 2011 and 2025 research. “It is rather more tough to calculate their precise plenty.”
Discovering an object’s precise mass requires figuring out its distance, in the same method to how transferring a magnifying glass nearer and farther distorts the obvious measurement of objects with out altering the variations between them.
Bennett and his colleagues in 2011 floated two situations for the pair of objects: Both it is a star and a planet, with the star barely much less huge than our solar and the planet 29 instances extra huge than Earth, or it is a much less distant rogue super- Jupiter towing a moon smaller than Earth.

For the brand new examine, researchers sought to seek out out what these two are and what they’re as much as greater than a decade later – utilizing knowledge from the Keck Observatory in Hawaii and the European Area Company’s Gaia satellite tv for pc.
They settled on a star system roughly 24,000 light-years away from Earth because the likeliest candidate. It is within the Milky Manner’s brilliant, densely populated central bulge of stars, the galactic downtown to our distant suburban perch.
Primarily based on its distance from the 2011 sign, the staff calculated how briskly the star is transferring, discovering its pace is greater than twice that of our solar.
That solely accounts for its two-dimensional movement as seen from Earth, although. It is also transferring towards or away from us, which is tougher to detect from our vantage, but would imply it is transferring even quicker.
That implies this star is perhaps quick sufficient to surpass the Milky Manner’s escape velocity, considered round 550 to 600 kilometers per second.
In that case, then it is headed for intergalactic house – though not for thousands and thousands of years, for the reason that Milky Manner is big and it is nonetheless just about proper within the center.
Whereas this photo voltaic system matches the profile of the 2011 objects, solely time will inform.
“To make sure the newly recognized star is a part of the system that prompted the 2011 sign, we would prefer to look once more in one other yr and see if it strikes the correct amount and in the correct route,” Bennett says.
If the star simply stays stationary, then we’ll know it isn’t contributing to the signal-causing system.
“That may imply the rogue planet and exomoon mannequin is favored,” explains astrophysicist Aparna Bhattacharya from the College of Maryland and NASA Goddard.
The examine was printed in The Astronomical Journal.