
A brand new AI mannequin that’s able to simultaneous evaluation of various pores and skin pictures can doubtlessly enhance the diagnostic accuracy of each dermatology and non-dermatology professionals.
A world analysis crew led by AI and machine studying consultants from Monash College developed a multimodal basis mannequin, referred to as PanDerm, designed as a medical resolution help software in dermatology. It could course of a number of pores and skin pictures without delay and supply diagnostic chance assessments.
The AI mannequin was educated on greater than two million pores and skin pictures of 4 sorts: close-up pictures, dermoscopic pictures, pathology slides, and complete physique pictures, which had been sourced from 11 establishments in several nations.
It was educated to carry out a variety of medical duties, together with total-body pores and skin most cancers detection and threat evaluation, most cancers recurrence and metastasis prediction, pores and skin sort evaluation, mole counting, lesion change monitoring, differential analysis of assorted pores and skin circumstances, and lesion segmentation.
The PanDerm crew concerned researchers and medical doctors from Alfred Well being, the College of Queensland, Princess Alexandra Hospital in Brisbane, Royal Prince Alfred Hospital, NSW Well being Pathology, the College of Florence in Italy, Medical College of Vienna in Austria, NVIDIA AI Know-how Centre in Singapore, and Hospital Common Universitario de Alicante in Spain.
FINDINGS
The researchers carried out diagnostic efficiency validations and three reader research to judge their mannequin, the findings of which have been printed in Nature Drugs.
Amongst notable findings was that the mannequin outperformed clinicians in detecting early-stage melanoma, probably the most aggressive sort of pores and skin most cancers, by 10%.
It was additionally discovered that the AI helped increase the accuracy of dermatologists in diagnosing pores and skin most cancers from dermoscopic pictures by 11% factors to 80%.
One other important discovering was that PanDerm enhanced the power of non-dermatologists to establish and differentiate pores and skin circumstances, reminiscent of inflammatory dermatoses and pigmentary problems, primarily based on pictures by 16.5%. These embrace generalists who routinely carry out preliminary pores and skin assessments: basic practitioners, basic drugs practitioners, and nursing and medical trial assistants.
Curiously, the mannequin was additionally discovered to surpass current fashions (reminiscent of SwAVDerm, SL-Imagenet, and DINOv2) in performing numerous medical duties associated to the evaluation of pores and skin most cancers and different pores and skin circumstances, even when educated with solely 10% of labelled information. Duties embrace threat stratification of lesions, phenotype evaluation, detection of lesion modifications and malignancy, multi-class most cancers analysis, lesion segmentation, and metastasis prediction and prognosis.
“Given restricted specialist entry in major care settings the place most pores and skin circumstances are initially evaluated, these findings point out PanDerm’s potential to deal with dermatological experience gaps throughout healthcare settings by way of each its technical capabilities and medical purposes. Importantly, throughout each human-AI collaboration research, PanDerm alone carried out equivalently to clinicians with PanDerm help in pores and skin most cancers analysis and even outperformed human-AI collaboration in differential analysis,” the authors stated.
“This phenomenon in all probability stems from clinicians’ selective incorporation of AI suggestions fairly than blind adherence, representing a balanced medical implementation during which practitioners keep their diagnostic autonomy whereas nonetheless benefiting from AI help,” they defined.
WHY IT MATTERS
Assessing pores and skin circumstances in medical follow includes quite a few duties – from threat assessments and picture evaluation to monitoring lesions and predicting outcomes. Whereas AI-powered medical help instruments are extensively accessible for dermatology, they continue to be restricted to single, remoted duties.
“The absence of built-in AI options able to supporting these numerous workflows at present hampers the sensible affect of AI in dermatology,” the researchers stated.
“Earlier AI fashions have struggled to combine and course of numerous information sorts and imaging strategies, decreasing their usefulness to medical doctors in several real-world settings,” Monash College affiliate professor Zongyuan Ge, one of many examine’s lead co-authors, was quoted as saying in a media launch.
The PanDerm crew’s examine, in accordance with H. Peter Soyer, one other lead co-author, has revealed the potential of a brand new multimodal basis mannequin to help pores and skin illness care in low-resource settings.
“The power of PanDerm lies in its skill to help current medical workflows. It may very well be significantly beneficial in busy or resource-limited settings, or in major care the place entry to dermatologists could also be restricted. We’ve seen that the software was additionally in a position to carry out strongly even when educated on solely a small quantity of labelled information, a key benefit in various medical settings the place normal annotated information is usually restricted,” stated the professor and the director of the Dermatology Analysis Centre on the College of Queensland.
Moreover, PanDerm may very well be indispensable in detecting the lethal and invasive melanoma early. “This sort of help might help earlier analysis and extra constant monitoring for sufferers liable to melanoma,” stated Victoria Mar, one of many examine’s lead co-authors and a professor and director of the Victorian Melanoma Service at Alfred Well being.
The analysis crew plans to conduct extra medical evaluations of their dermatology basis mannequin with a deal with guaranteeing equitable efficiency throughout totally different affected person populations and healthcare settings.
THE LARGER TREND
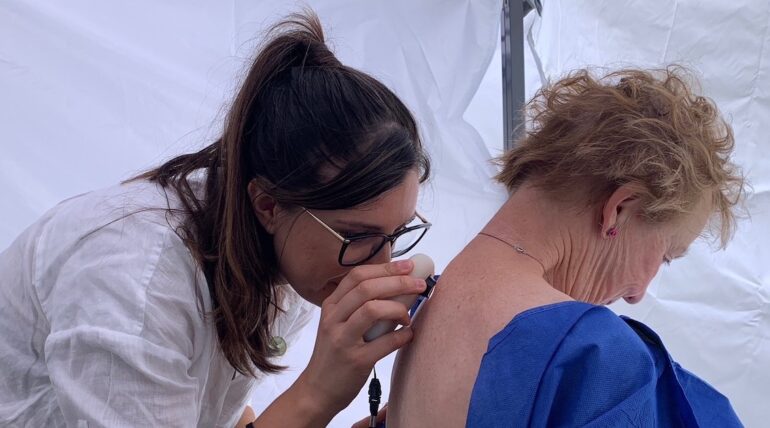
It is usually in Australia the place the world’s first AI-driven pop-up skincare clinic was set as much as detect pores and skin cancers reminiscent of melanoma early. Roughly two of three Australians could be recognized with some type of pores and skin most cancers of their lifetime. Primarily based on authorities statistics, round 400,000 instances are reported every year. The nurse-led pop-up clinic by well being charity Pores and skin Verify Champions goals to carry that quantity down by half and enhance pores and skin screening by 1 / 4 with the help of AI.
Exterior Australia, lately, South Korea has accredited its first domestically developed AI-powered smartphone utility for pores and skin most cancers analysis. The canofyMD SCAI by LifeSemantics obtained regulatory approval from the Ministry of Meals and Drug Security in June final 12 months.